静态库
iOS常见的库文件格式:
* `.a` : 静态库
* `.dylib` : 动态库
* `.tdb` : 动态库
* `.framework` :可以是静态库,也可以是动态库,可以静动结合
* `.xcframework` :2019年苹果新出的针对不同架构`x86/armv7/arm64`的库文件格式,framework的升级版,可以多架构一起,在打包时针对那个架构就链接那个架构的格式。2
3
4
5
静态库文件是什么?其本质是所有.o文件的合集,通过ar 指令可以查看和修改静态库文件。比如使用ar -t libAFNetworking.a查看 AFNetworking 的静态库文件,结果如下:
AFAutoPurgingImageCache.o
AFHTTPSessionManager.o
AFImageDownloader.o
AFNetworkActivityIndicatorManager.o
...2
3
4
5
根据查看结果我们可以确定,静态库的本质就是
.o文件的合集
calng命令参数
* `-x`:指定编译文件语言类型,不指定语言也可以,clang 会自动识别语言
* `-g`:生成调试信息
* `-c`:生成目标文件,只运行preprocess, compile, assemble,不链接
* `-o`:输出文件
* `-isysroot`: 使用的SDK路径
* `-I<directory>`: 在指定目录寻找头文件,对应Xcode中的`header search path`
* `-L <dir>`: 指定库文件路径(.a\.dy1ib库文件),对应Xcode中的`library search paths`
* `-l<library_name>`: 指定链接的库文件名称(.a\.dylib库文件),对应Xcode中的`other link flags -lAFNetworking`
* `-F<directory>`: 在指定目录寻找framework头文件
* `-framework <framework_name>`在指定链接的framework名称,生成相应的LLVM文件格式,来进行链接时间优化,当我们配合着`-S`使用时,生成汇编语言文件。否则生成`bitcode`格式的目标文件
* `-flto=<value>`设置LTO的模式,它值有`full` or `thin`,默认是`full`
* `-f1to=full`,默认值,单片 (monolithic) LTO通过将所有输入合并到单个模块中来实现此目的
* `-flto=thin`,使用`ThinLTo`代替
* `-emit-llvm` 对汇编程序和目标文件使用 LLVM 表示
* `-install-name` 指定动态库初次安装时的默认路径,向`LC_ID_DYLIB`添加安装路径,该路径作为dyld定位该库。
* `-Xlinker <arg>` 将参数传递链接器2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
链接静态库的例子
例子很简单,.m文件中用到了静态库AFNetworking,我们使用clang编译器将下面的代码编译成可执行文件。
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import <AFNetworking.h>
int main(){
AFHTTPSessionManager *manager = [AFHTTPSessionManager manager];
NSLog(@"testApp----%@", manager);
return 0;
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- 通过clang编译器先将文件编译成 .o 文件
clang -x objective-c \
-target x86_64-apple-macos11.1 \
-fobjc-arc \
-isysroot /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX12.sdk \
-c test.m -o test.o2
3
4
5
提示我们找不到#import <AFNetworking.h>头文件。我们需要将静态库的位置告诉编译器,-I参数后紧跟静态库文件位置
clang -x objective-c \
-target x86_64-apple-macos11.1 \
-fobjc-arc \
-isysroot /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX12.sdk \
-I ./AFNetworking \
-c test.m -o test.o2
3
4
5
6
每条指令对应的含义如下:
将test.m编译成test.o:
* 1. 使用OC
* 2. 生成的是X86_64_macOS架构的代码。
* Big Sur是:`x86_64-apple-macos11.1`
* 之前是:`x86_64-apple-macos10.15`
* arm64是`arm64-apple-macos11`
* 3. 使用ARC
* 4. 使用的SDK的路径在:
* Big Sur是:`/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX11.1.sdk`
* 之前是:`/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX10.15.sdk`
* 5. 用到的其他库的头文件地址在./Frameworks
* 6. 将`.c`文件编译成`.o`文件2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
- 生成可执行文件
-L./StaticLibrary在当前目录的子目录 StaticLibrary 查找需要的库文件-lAFNetworking链接的名称为libAFNetworking的动态库或者静态库。查找规则:先找lib+<library_name>的动态库,找不到,再去找lib+<library_name>的静态库,还找不到,就报错.
clang -target x86_64-apple-macos11.1 \ -fobjc-arc \ -isysroot /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX12.sdk \ -L./AFNetworking \ -lAFNetworking \ test.o -o test1
2
3
4
5
6
如何证明静态库就是.o文件的合集
将下面两个 .m 文件编译成 .o 文件, TestExample.m 文件制作成静态库, test.m 文件制作成可执行文件。在 test.m 文件中对 TestExample 文件进行引用。TestExample.m 文件在同目录下的子目录 StaticLibrary 文件夹下。
- TestExample.m文件代码
#import "TestExample.h"
@implementation TestExample
- (void)lg_test:(_Nullable id)e {
NSLog(@"TestExample----");
}
@end2
3
4
5
6
- test.m文件代码
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "TestExample.h"
int main(){
NSLog(@"testApp----");
TestExample *manager = [TestExample new];
[manager lg_test: nil];
return 0;
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- 将 TestExample.m 文件 编译成.o文件
clang -x objective-c \
-target x86_64-apple-macos11.1 \
-fobjc-arc \
-isysroot /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX12.sdk \
-c TestExample.m -o TestExample.o2
3
4
5
- 编译完成后将
TestExample.o后缀修改为TestExample.dylib,然后删除后缀,将名称改为libTestExample,这里名字前加lib是因为-l参数会找lib开头的库文件 - 将 test.m 文件 编译成.o文件
clang -x objective-c \
-target x86_64-apple-macos11.1 \
-fobjc-arc \
-isysroot /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX12.sdk \
-I./StaticLibrary \
-c test.m -o test.o2
3
4
5
6
- 将 test.o 文件编译成 可执行文件,使用
lipo -archs xxx可以查看支持的框架
clang -target x86_64-apple-macos11.1 \
-fobjc-arc \
-isysroot /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX12.sdk \
-L./StaticLibrary \
-lTestExample \
test.o -o test2
3
4
5
6
- 使用
lldb进行验证- 终端切换到当前目录下,输入
lldb - 输入
file test加载可执行文件 - 输入
r运行加载的可执行文件,结果如下:
mMacBook-Pro-2 Desktop % lldb (lldb) file test Current executable set to '/Users/x/Desktop/test' (arm64). (lldb) r Process 54869 launched: '/Users/x/Desktop/test' (arm64) 2022-11-15 14:36:02.987892+0800 test[54869:1324122] testApp---- 2022-11-15 14:36:02.988452+0800 test[54869:1324122] TestExample---- Process 54869 exited with status = 0 (0x00000000)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 - 终端切换到当前目录下,输入
静态库合并 libtool
多个静态库合并需要使用libtool -static -o <OUTPUT NAME> <LIBRARY_1> <LIBRARY_2>指令,比如合并
libtool -static -o libnew.a libAFNetworking.a libSDWebImage.aFramework
Framework 可以是动态库,也可以是静态库。当它是静态库时包含 Headers(头文件)、静态库文件、签名、资源文件。 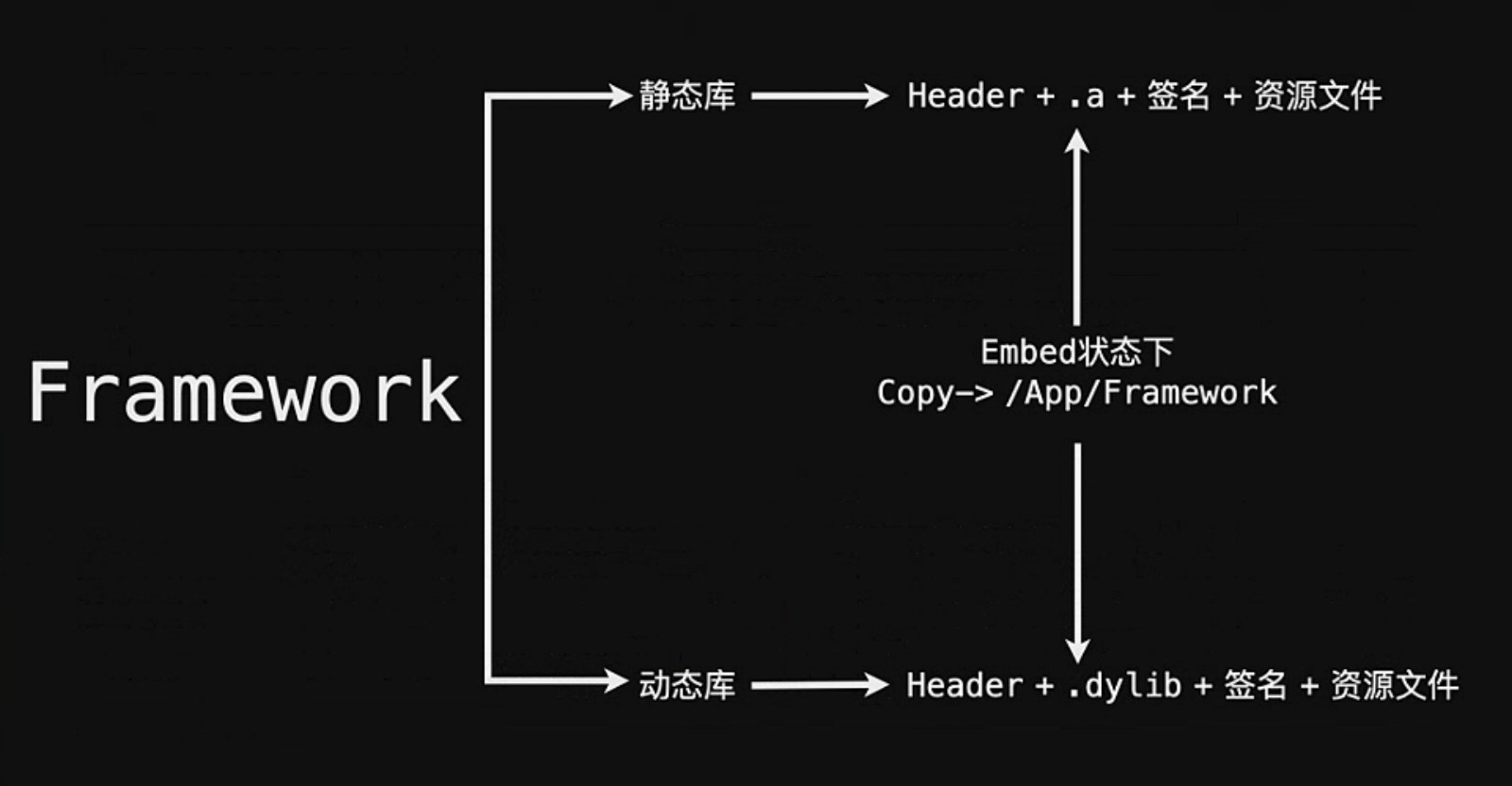
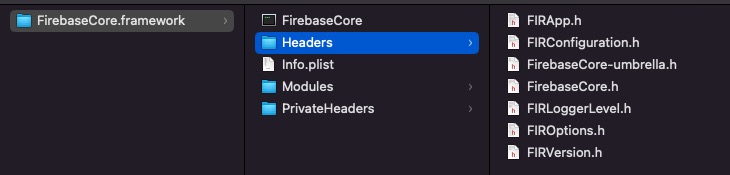
现在我们来手动制作一个Framework,首先需要创建TestExample.framework文件夹,文件夹内包含 Headers文件, 文件夹内包含 .h 头文件。
- 将 TestExample.m 文件 编译成.o文件
clang -x objective-c \
-target x86_64-apple-macos11.1 \
-fobjc-arc \
-isysroot /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX12.sdk \
-c TestExample.m -o TestExample.o2
3
4
5
- 使用
ar指令将TestExample.o制作成静态库格式,将制作好的静态库放到TestExample.framework文件夹
ar -rc TestExample TestExample.o
// ar 压缩目标文件,并对其进行编号和索引,形成静态库。同时也可以解压缩静态库,查看有哪些目标文件
-r: 向 TestExample 添加或者替换文件
-c: 不输出任何信息
-t: 列出包含的目标文件2
3
4
5
6
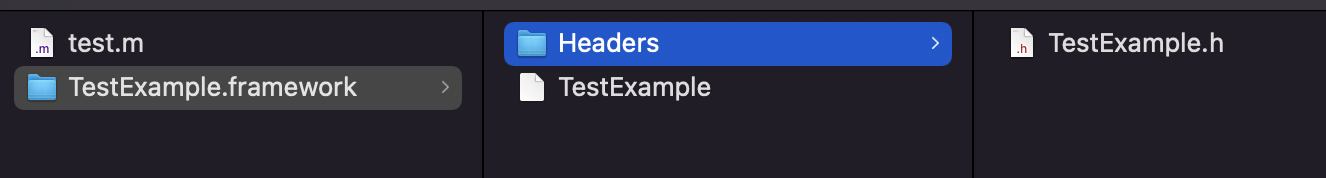 3. 将 test.m 文件 编译成.o文件
3. 将 test.m 文件 编译成.o文件
clang -x objective-c \
-target x86_64-apple-macos11.1 \
-fobjc-arc \
-isysroot /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX12.sdk \
-I./TestExample.framework/Headers \
-c test.m -o test.o2
3
4
5
6
- 将 test.o 文件编译成 可执行文件
clang -target x86_64-apple-macos11.1 \
-fobjc-arc \
-isysroot /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX12.sdk \
-F./ \
-framework TestExample \
test.o -o test2
3
4
5
6
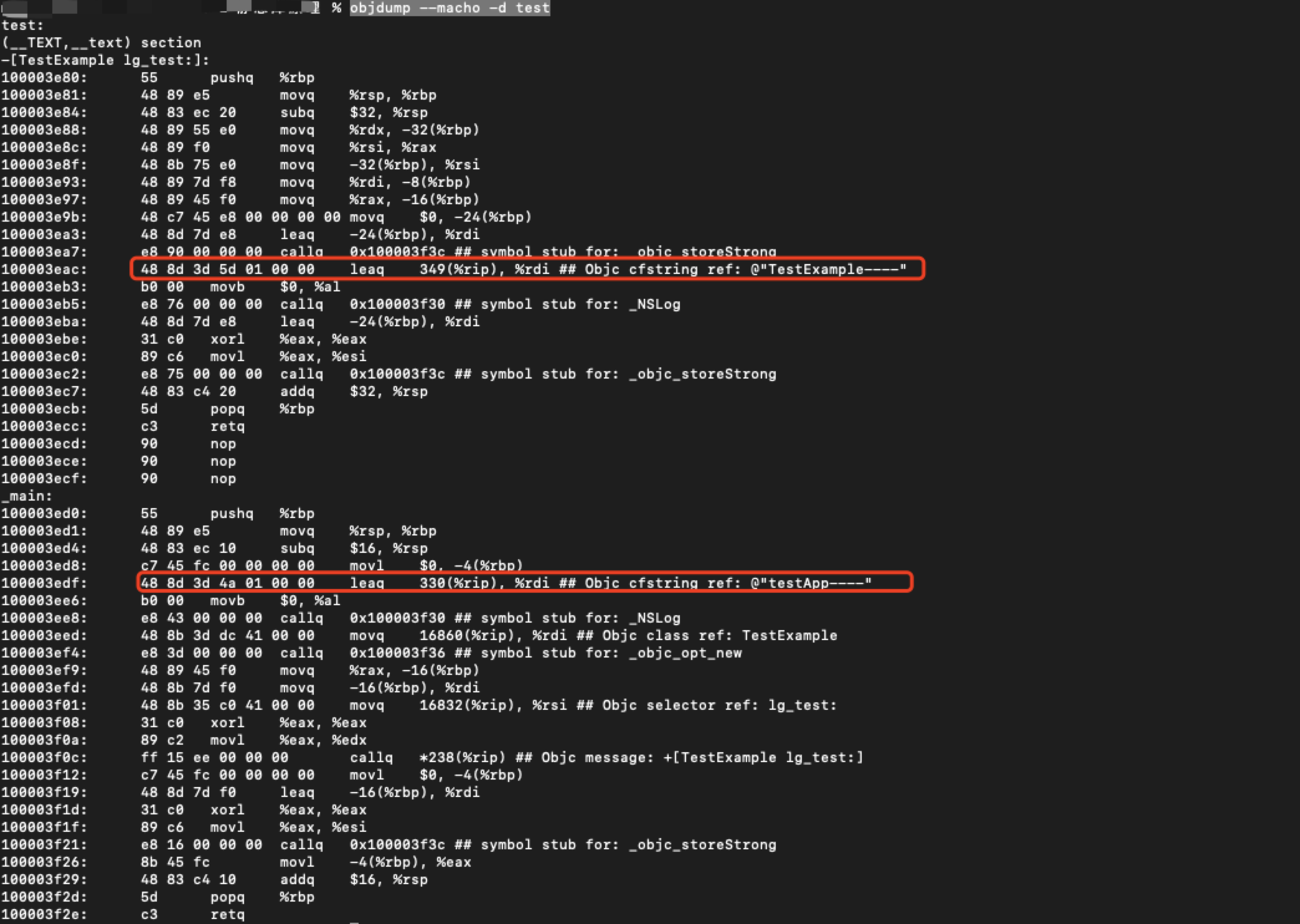
使用objdump --macho -d test可查看Mach-O可执行文件的代码段,如下图:
静态库内使用分类
我们在使用 Cocoapods 加载第三方库时,会在 Xcode -> Build Settings -> Other Link Flags 中添加 -ObjC。这是为啥勒?
我们知道分类是在运行时动态创建的,而-dead strip会在链接的过程中剥离没有使用的分类方法,导致方法找不到的崩溃,解决方式就是在链接过程中使用
`-all_load` 所有的都加载
` -ObjC` 只保留OBJC的代码
`-force_load `:那些静态库 -》dead strip2
3
- 用一个例子进行展示,首先创建一个Framework静态库,包含 LGOneObject 类和分类,在类中调用分类的方法。
- LGOneObject 类
// .h
@interface LGOneObject : NSObject
- (void)lg_test;
@end
// .m
#import "LGOneObject.h"
#import <LGOneObject+Category.h>
@implementation LGOneObject
- (void)lg_test {
[self lg_test_category]; // 调用分类的方法
}
@end2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
- LGOneObject 分类
// .h
@interface LGOneObject (Category)
- (void)lg_test_category;
@end
// .m
@implementation LGOneObject (Category)
- (void)lg_test_category {
NSLog(@"lg_test_category");
}
@end2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
在 Xcode -> Build Settings -> Mach-O Type 设置成静态库 Static Library,在 Xcode -> Build Phases -> Headers中公开 LGOneObject.h 文件 2. 创建一个新的iOS项目 3. 打开静态库项目,点击Xcode导航栏 -> File -> Save As Workspace,创建的 Workspace 需要跟静态库在同一目录下, 删除Xcode中选中的文件,点击左下角 + 号按钮,选择刚才创建的Workspace名称,添加时选择创建的iOS项目。如下图

添加后需要关闭Xcode,打开Workspace文件,静态库和iOS项目都显示在Xcode中。 4. 编译静态库,将静态库导入到iOS项目,在项目中使用lg_test方法
#import "ViewController.h"
#import <LGObject/LGOneObject.h>
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
[[LGOneObject new] lg_test];
}
@end2
3
4
5
6
7
8
编译没有问题,但是在运行的时候,会造成崩溃提示找不到lg_test方法。这是因为 -dead strip是在链接的时候对无用代码进行剥离,而分类是动态加载的,解决方法就是在链接过程中告诉链接器有些代码不需要剥离。
- 创建
Configuration Settings File文件,通过OTHER_LDFLAGS告诉链接器不要剥离,这三种方法都可以:
// -Xlinker -all_load:不dead strip,加载全部代码
// -Xlinker -ObjC:加载全部OC相关代码,包括分类
// -force_load: 要加载那个静态库的全部代码
FRAMEWORK_PATH = ${BUILD_DIR}/$(CONFIGURATION)$(EFFECTIVE_PLATFORM_NAME)/LGObject.framework/LGObject
OTHER_LDFLAGS = -Xlinker -force_load ${FRAMEWORK_PATH}2
3
4
5
6
-Xlinker表示传递参数给链接器,clang是编译器, -Xlinker意思是后面的参数时传递给链接器ld的。链接器默认是no_all_load
或者直接在Xcode -> Build Settings -> Other Link Flags 中添加 -ObjC同样也可以。