objc_msgSend函数
当我们使用[ ]调用方法时,底层是通过objc_msgSend()函数进行调用的,这也是OC特有的消息机制,方法调用是通过消息传递的形式进行的。比如下面的代码:
NSObject *objc = [[NSObject alloc] init];
[objc class];
[NSObject class];2
3
通过xcrun -sdk iphoneos clang -arch arm64 -rewrite-objc main.m -o main.cpp命令转成c++代码
objc_msgSend(objc, sel_registerName("class"));
objc_msgSend(objc_getClass("NSObject"), sel_registerName("class"));
// OC的方法调用:消息机制 给方法调用者发送消息 sel_registerName("class") 等价于 @selector(class)
// 消息接收者(receiver): objc 、objc_getClass("NSObject")
// 消息名称: class2
3
4
5
6
objc_msgSend需要两个参数,一个是消息接收者(receiver),一个是消息名称(SEL)。我们将通过阅读源码、消息发送、动态解析方法、消息转发 这几个步骤逐步分析OC的消息机制。
通过源码认识 objc_msgSend
objc_msgSend方法是汇编编写的,真机只看objc-msg-arm64.s文件即可,ENTRY _objc_msgSend是方法的入口,代码片段来自于objc4-818.2
// _objc_msgSend 方法的入口
ENTRY _objc_msgSend
UNWIND _objc_msgSend, NoFrame
cmp p0, #0 // 消息接受者是否为nil,为nil时ret
b.eq LReturnZero
ldr p13, [x0] // p13 = isa
GetClassFromIsa_p16 p13, 1, x0 // p16 = class
LGetIsaDone:
// 调用imp或objc_msgSend_uncached,因为传入的NORMAL 为0,所以调用的是 __objc_msgSend_uncached
CacheLookup NORMAL, _objc_msgSend, __objc_msgSend_uncached
LReturnZero: // 返回
...
ret
END_ENTRY _objc_msgSend2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
整个查找路径是: ENTRY _objc_msgSend -> __objc_msgLookup_uncached ->MethodTableLookup -> _lookUpImpOrForward
我们发现最后会调用_lookUpImpOrForward方法,汇编中调用函数会在函数前添加下划线,全局搜索lookUpImpOrForward,对应的函数实现如下,代码片段来自于objc4-818.2:
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
{
// 获取转发的imp
const IMP forward_imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
IMP imp = nil;
Class curClass;
....
cls = realizeAndInitializeIfNeeded_locked(inst, cls, behavior & LOOKUP_INITIALIZE);
curClass = cls;
for (unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();;) {
if (curClass->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true)) {
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (imp) goto done_unlock;
curClass = curClass->cache.preoptFallbackClass();
} else {
// 方法列表
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
imp = meth->imp(false);
goto done;
}
// 找不到方法并且方法解析器也无效时,使用转发
if ((curClass = curClass->getSuperclass()) == nil) {
imp = forward_imp;
break;
}
}
....
// Superclass cache.
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (imp == forward_imp) {// 在超类的forward::方法中找到,停止搜索,不缓存,首先调用此类的解析器
break;
}
if (imp) { // 在超类中找到该方法。 将其缓存在此类中
goto done;
}
}
// 找不到实现。 尝试一次方法解析器
if (behavior & LOOKUP_RESOLVER) {
behavior ^= LOOKUP_RESOLVER;
return resolveMethod_locked(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
done:
if ((behavior & LOOKUP_NOCACHE) == 0) {
while (cls->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true)) {
cls = cls->cache.preoptFallbackClass();
}
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
}
done_unlock:
runtimeLock.unlock();
if ((behavior & LOOKUP_NIL) && imp == forward_imp) {
return nil;
}
return imp;
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
通过阅读lookUpImpOrForward方法,我们会发现 objc_msgSend的执行流程可以分为3大阶段
- 消息发送
- 动态方法解析
- 消息转发
消息发送
通过阅读lookUpImpOrForward方法,来看objc_msgSend函数的调用顺序:
- 消息接收者(receiver)是否为nil,如果为nil,直接return。如果不为空 -> 执行步骤 2
- receiver 通过isa指针找到 receiverClass ,在类对象缓存中(
cache)查找方法,如果找到方法直接调用,如果没有找到 -> 执行步骤 3 - 从当前类的
class_rw_ext_t中查找方法,如果找到方法直接调用,如果没有找到 -> 执行步骤 4 - receiverClass 通过 superclass指针 找到 superClass ,从
superclass的缓存中(cache)查找方法,如果找到方法直接调用。如果没有找到 -> 执行步骤 5 - 从父类的
class_rw_ext_t中查找方法,如果找到方法直接调用。如果没有找到 -> 执行步骤 6 - 查看上层是否还有父类,如果有父类 -> 执行步骤 4
- 如果没有父类,进入 -> 动态方法解析
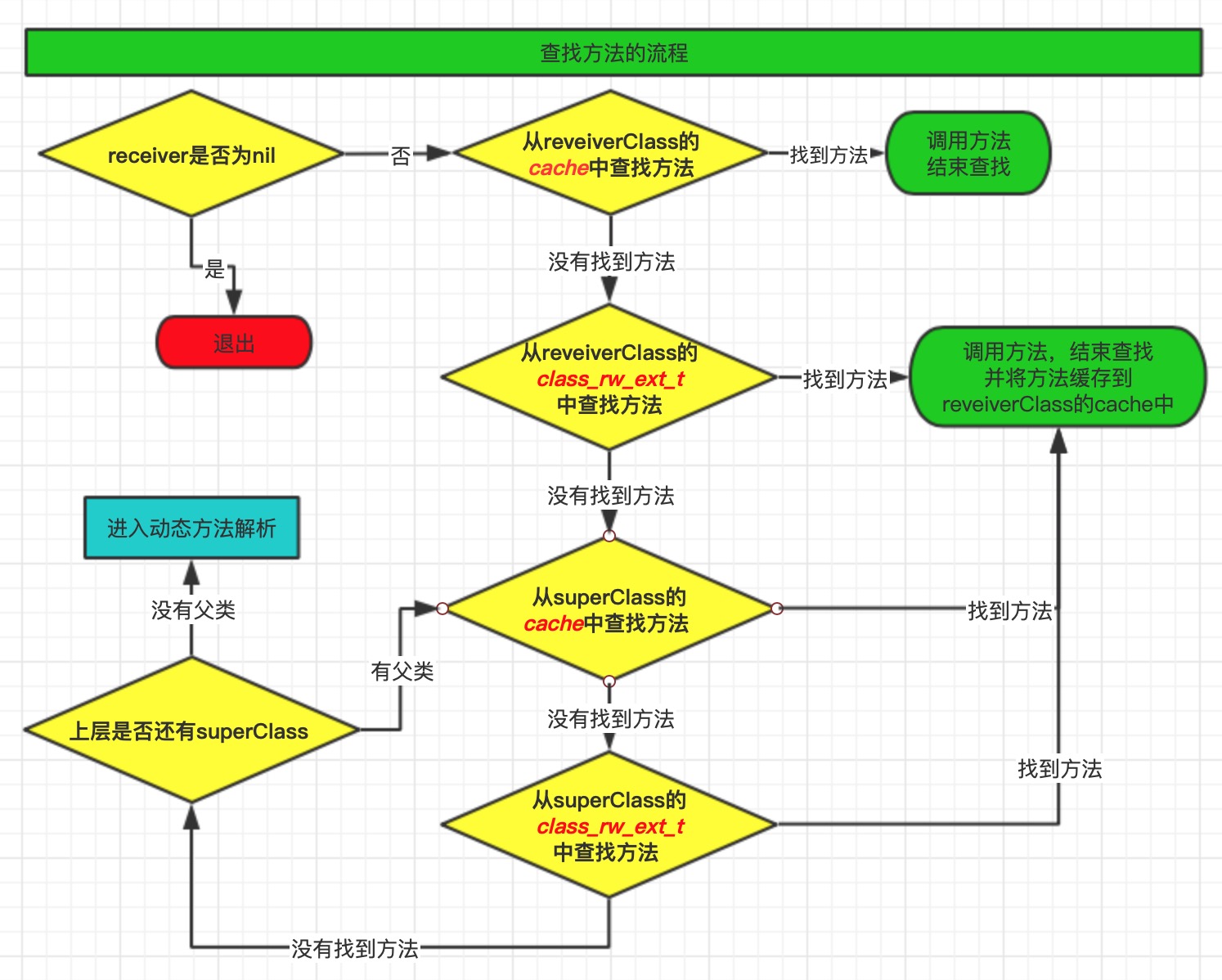 从
从class_rw_ext_t中查找方法有两种方式:
- 方法经过排序的,二分查找
findMethodInSortedMethodList函数 - 方法没有排序的,遍历查找
findMethodInUnsortedMethodList函数
动态方法解析
动态方法解析是调用resolveMethod_locked函数,开发者可以通过实现+resolveInstanceMethod:和+resolveClassMethod:两个方法,来动态添加方法实现。动态解析过后,会重新走“消息发送”的流程,从"receiverClass的cache中查找方法"这一步开始执行
static NEVER_INLINE IMP
resolveMethod_locked(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
{
if (! cls->isMetaClass()) {
resolveInstanceMethod(inst, sel, cls);
}
else {
// try [nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel]
// and [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
resolveClassMethod(inst, sel, cls);
if (!lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(inst, sel, cls)) {
resolveInstanceMethod(inst, sel, cls);
}
}
// lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache 最终会再次调用 lookUpImpOrForward 函数
return lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
动态方法解析的步骤,流程如下图:
- 判断是否曾经有过方法解析,如果有,直接执行消息转发,如果没有 -> 执行步骤2
- 通过实现
+resolveInstanceMethod:和+resolveClassMethod:两个方法,来动态添加方法实现。并且标记为已经动态解析。 - 动态方法解析完成后,重新进入消息发送阶段
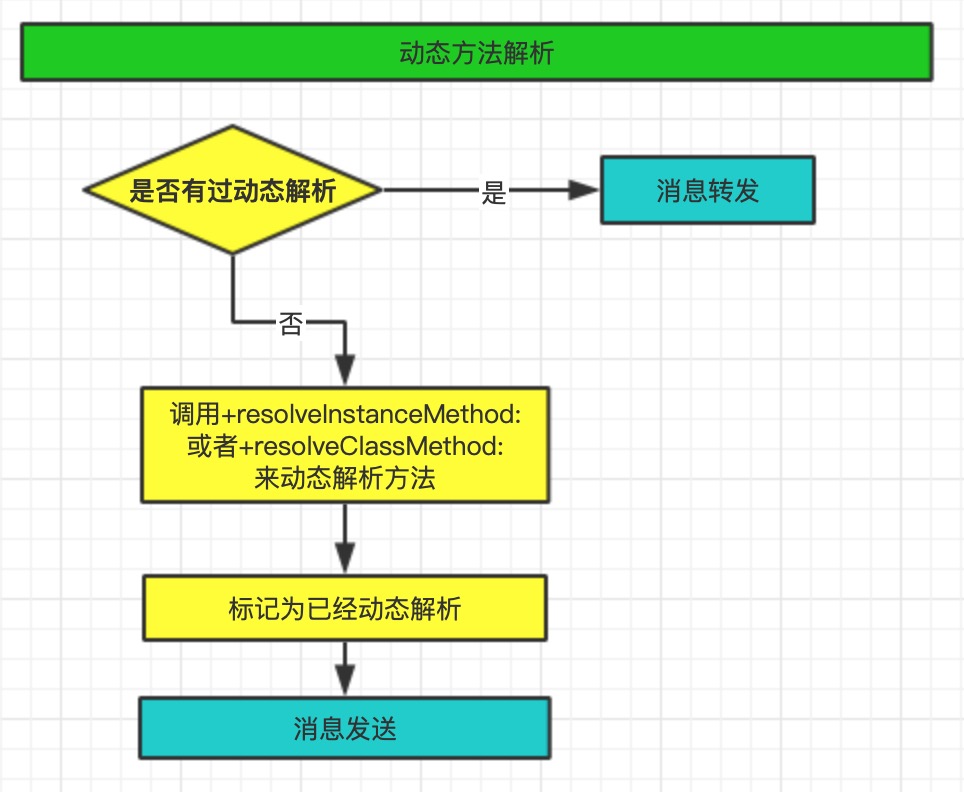
在动态方法解析中添加方法避免程序崩溃
定义一个 Person 类,声明两个方法-sayHello和+sayHello,只做声明不做内部实现,添加+resolveInstanceMethod:和+resolveClassMethod:方法,在这里向Person动态添加方法
#import "Person.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation Person
- (void)other{
NSLog(@"%s --",__func__);
}
void test(id self,SEL _cmd){
NSLog(@"%s",__func__);
}
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel{
if (sel == @selector(sayHello)) {
// 这里是添加实例方法,需要将方法添加到类对象中。因为当前就是在+号方法中,self本身就是类对象
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(other));
class_addMethod(self, sel, method_getImplementation(method), method_getTypeEncoding(method));
// 也可以动态添加c语言的方法
// class_addMethod(self, sel, (IMP)test, "v@:");
return YES;
}
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}
+ (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel{
if (sel == @selector(sayHello)) {
//注意:这里是添加类方法,因为类方法是存储在元类对象中,所以需要给元类对象添加方法
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(other));
class_addMethod(object_getClass(self), sel, method_getImplementation(method), method_getTypeEncoding(method));
return YES;
}
return [super resolveClassMethod:sel];
}
@end2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
Method 详解
Method跟method_t结构体很类似,官方定义typedef struct objc_method *Method;我们可以把它理解成struct method_t*,比如也可以使用下面的代码给Person类动态添加方法:
struct method_t {
SEL name;
char * types;
IMP imp;
};
- (void)other{
NSLog(@"%s --",__func__);
}
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel{
if (sel == @selector(sayHello)) {
struct method_t *method = (struct method_t*)class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(other));
class_addMethod(self, sel, method->imp, method->types);
NSLog(@"%s -- %s --%p",sel_getName(method->name),method->types,method->imp);//other -- v16@0:8 --0x100003bd0
return YES;
}
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
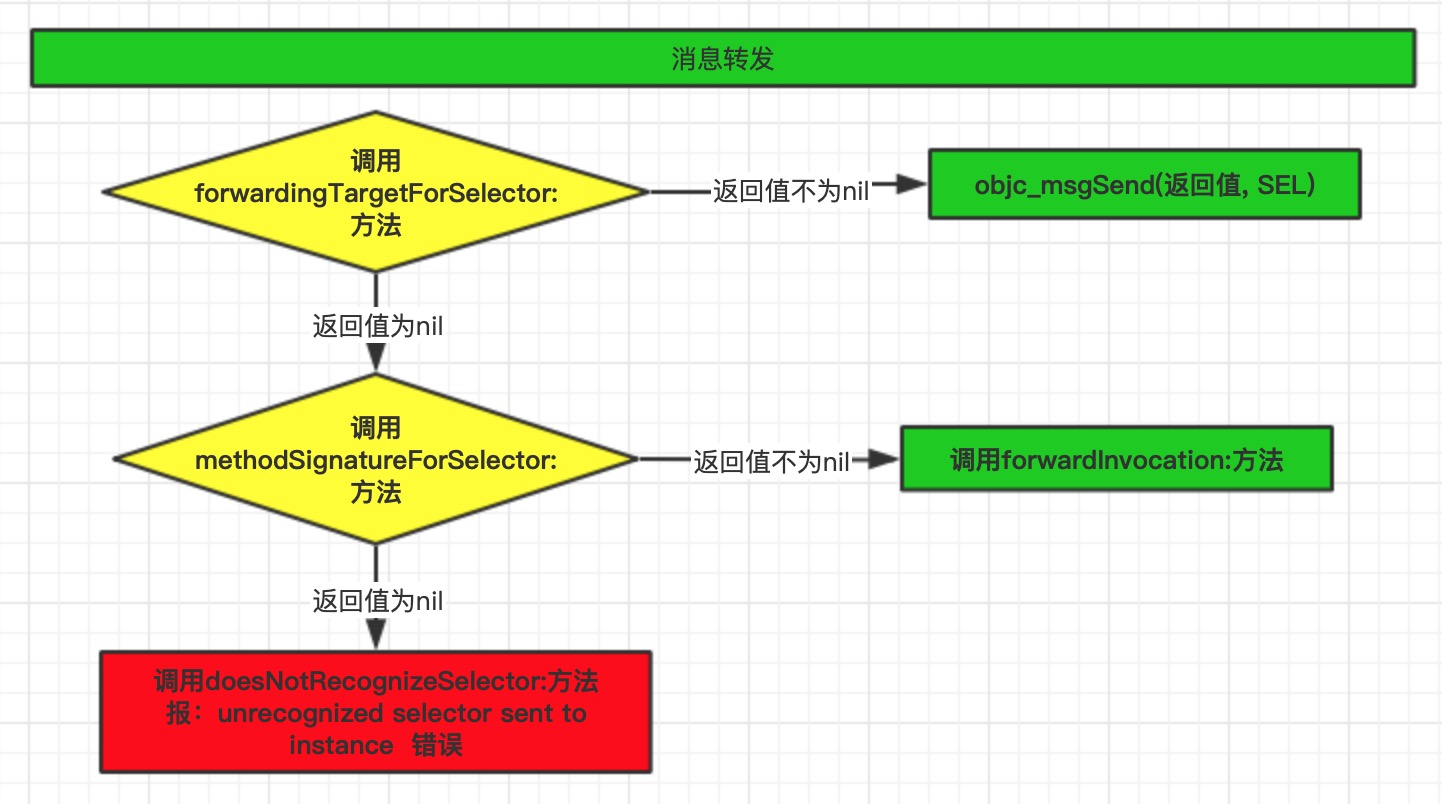
消息转发
当消息发送和动态方法解析都不能处理消息时,会来到消息转发_objc_msgForward_impcache。我们在源码中找不到_objc_msgForward_impcache方法的具体实现,可以通过打断点的方式判断系统都调用了什么方法。在这之前我们先看一下消息转发流程:
- 调用
forwardingTargetForSelector:方法将消息转发给别的对象处理(转发的对象要有处理消息的能力),如果返回值为nil,执行步骤2 - 调用
methodSignatureForSelector:方法,如果返回值不为nil,调用forwardInvocation:方法 。如果返回nil,执行步骤3 - 调用
doesNotRecognizeSelector:方法,报经典错误unrecognized selector sent to instance
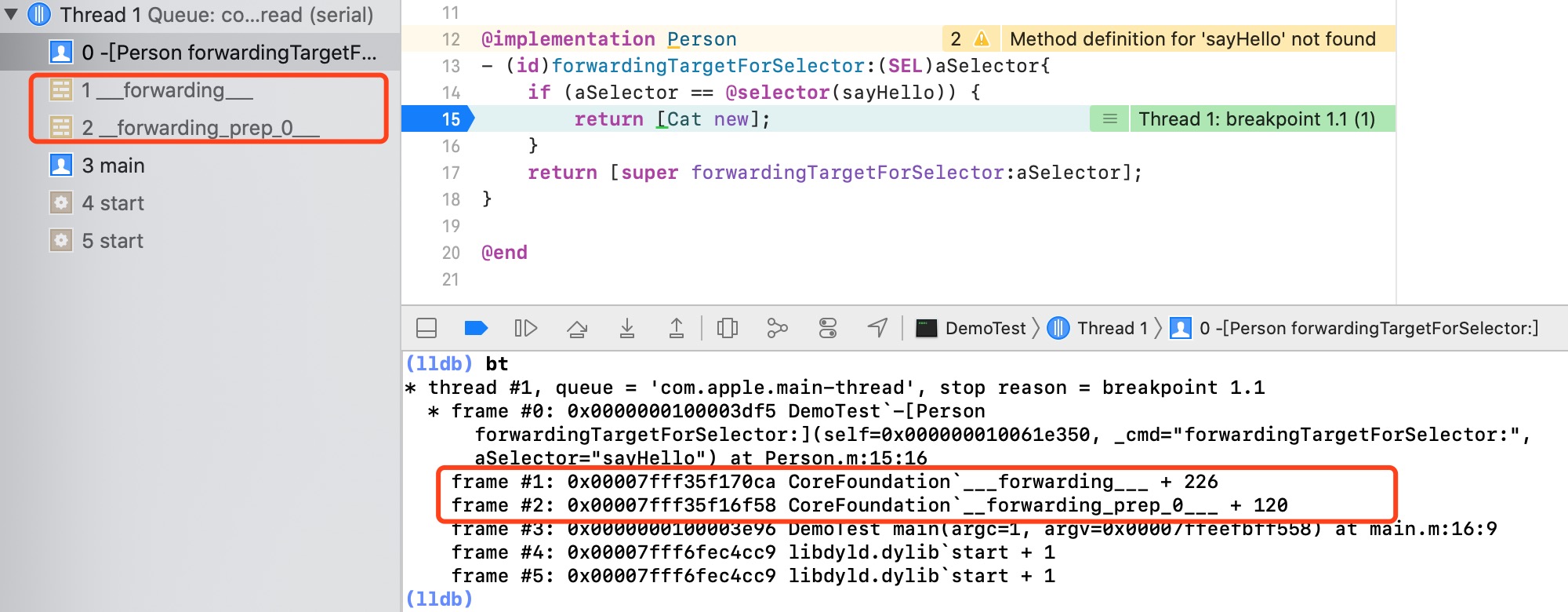
我们知道了消息的转发流程,在forwardingTargetForSelector:方法内打断点,打印堆栈信息,看一下系统是通过什么函数进行调用的,通过打印堆栈我们看到,方法是被___forwarding___函数调用的,我们基本可以确定消息转发是从___forwarding___函数开始的。
forwardingTargetForSelector: 方法
#import "Person.h"
#import "Cat.h"
@implementation Person
// 将Person类的消息转发给Cat类
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
if (aSelector == @selector(sayHello)) {
return [Cat new];
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
+ (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
if (aSelector == @selector(sayHello)) {
return [Cat class];
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
@end2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
methodSignatureForSelector:方法 将消息转发给其他对象处理
如果没有实现forwardingTargetForSelector:方法或返回值为nil的情况下,会来到methodSignatureForSelector:方法,要求返回一个方法签名,也就是mtehod_t结构体中的types,比如-(void)sayHello;的方法签名是v16@0:8。
如果methodSignatureForSelector:方法返回值不为nil,会调用forwardInvocation:方法,在这里我们可以做任何事情,可以转发给其他对象消息,也可以只打印信息。不会造成崩溃。
// 方法签名: 返回值类型、参数类型
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
if (aSelector == @selector(sayHello)) {
return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v16@0:8"];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
// NSInvocation 封转了一个方法调用,包括方法调用者、方法名、方法参数
// anInvocation.target 方法调用者
// anInvocation.selector 方法名
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation{
if (anInvocation.selector == @selector(sayHello)) {
anInvocation.target = [Cat class];
[anInvocation invoke];
// 或者 [anInvocation invokeWithTarget:[Cat class]];
}
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
也可以在forwardInvocation:方法中通过NSInvocation获取参数和返回值,获取参数时需要注意:系统会默认在方法中带self和_cmd两个参数,我们自己传的参数下标是从2开始的,如果下标越界,会造成崩溃。
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
if (aSelector == @selector(sayHi:)) {
// 这里使用一个小技巧,因为cat类中有sayHi方法,可以直接使用cat生成方法签名
return [[Cat new] methodSignatureForSelector:@selector(sayHi:)];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation{
if (anInvocation.selector == @selector(sayHi:)) {
// 获取参数,参数书序 receiver、selector、other arguments
int hi;
[anInvocation getArgument:&hi atIndex:2];
// 注意必须消息调用之后才会有返回值
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:[Cat new]];
// 获取返回值
int ret;
[anInvocation getReturnValue:&ret];
NSLog(@"%d --%d",hi,ret); //100 --100
}
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
+methodSignatureForSelector:和+forwardInvocation:也有类方法
+ (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
if (aSelector == @selector(sayHello)) {
return [[Cat class] methodSignatureForSelector:@selector(sayHello)];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
+ (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation{
if (anInvocation.selector == @selector(sayHello)) {
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:[Cat class]];
}
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11