CSS 布局
布局有三种方式: 常规流、浮动、绝对定位。常规流中包含 行级、块级、表格布局、Flexbox、Grid布局。
默认情况下,元素都是按照normal flow(标准流、常规流、正常流、文档流【document flow】)进行排布
* 从左到右、从上到下按顺序摆放好
* 默认情况下,互相之间不存在层叠现象2
在标准流中,可以使用
margin、padding对元素进行定位.
如果不想使用标准流,修改元素position的值。
* `static`: 默认值,相当于取消定位属性,或者不设置定位属性
* `relative`: 相对定位,元素占据的文档流位置不变,可以通过left、right、top、bottom进行定位,定位参照对象是元素自己原来的位置。
* `absolute`: 绝对定位,元素脱离文档流,不占据文档流的位置,相对与显示屏幕的宽高进行定位
* `fixed`: 固定定位,元素脱离文档流,不占据文档流位置,相对与窗口进行定位
* `sticky`: 粘性定位
* `inherit`: 从父元素集成position属性的值2
3
4
5
6
relative 相对定位
使用相对定位之后,元素设置此属性之后仍然处在文档流中,不影响其他元素的布局。可以通过left、right、top、bottom进行定位,元素相对于原来位置进行偏移,宽高不变。
通过将一个大图片居中的方式进行举例,图片大小是1920 x 489。div是浏览器宽度,图片超出div部分需要进行裁剪overflow: hidden;。先将img向左移动图片大小一半的距离left: -960px;,然后设置左间距是div的一半margin-left: 50%就会居中。
<style>
body{
margin: 0;
}
.box{
height: 489px;
background-color: red;
overflow: hidden; /*因为图片过大,超出父元素部分进行隐藏*/
}
.box img{
position: relative;
margin-left: 50%; /* 设置左侧间距为div宽度的一半 */
left: -960px; /* 让图片向左移动自身一半的像素 */
/* transform: translate(-50%); 设置translate也可以, translate的百分比是相对于自身大小的 */
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="box">
<img src="./imgs/mhxy.jpg" alt="">
</div>
</body>2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
fixed 固定定位
元素脱离标准流,可以通过left、right、top、bottom 进行定位,定位参照对象是视口(viewport)。当画布滚动时,固定不动。
<style>
.box{
width: 120px;
height: 5000px;
background-color: red;
}
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
right: 50px;
bottom: 50px;
background-color: gold;
position: fixed;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="box"> </div>
<div class="box1"> </div>
</body>2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
absolute 绝对定位
绝对定位是脱离文档流位置的.不区分行内元素/块级元素/行内块级元素,可以通过left、right、top、bottom进行定位。定位参照对象是最邻近的定位祖先元素。如果找不到这样的祖先元素,参照对象是视口。
在绝大数情况下,子元素的绝对定位都是相对于父元素进行定位,如果希望子元素相对于父元素进行定位,又不希望父元素脱标,常用解决方案是:
* 父元素设置`position: relative`(让父元素成为定位元素,而且父元素不脱离标准流)
* 子元素设置`position: absolute`2
绝对定位的一些特点:
1. 元素会脱离文档流。脱离文档流后原来的位置相当于是空的,下面的元素会来占据它的位置。
2. 元素在没有定义宽度的情况下,宽度由元素里面的内容决定,效果和用float方法一样。
3. 设置left或者top时,如果父元素没有相对或者决定定位的情况下,元素相对于根元素定位
4. 如果父元素设置了相对定位或绝对定位,元素会根据离自己最近的父元素进行定位2
3
4
对于普通元素来说,父元素的宽度 = 子元素的际占用宽度 + left + right。对于绝对定位元素来说,定位参照对象的宽度 = 绝对定位元素的实际占用宽度 + left + right + margin-left + margin-right,举一个例子
<style>
.box{
width:800px
height: 200px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
}
.continer{
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: gold;
position: absolute;
}
</style>
<div class="box">
<div class="continer"> </div>
</div>2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
我们只给 continer 设置了宽高,没有设置left、right、margin-left、margin-right,计算方式 800 = 200 + 0 + 0 + 0 + 0;。如果想让 continer 水平居中。可以设置以下代码
<style>
.continer{
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
left: 0px;
right: 0px;
margin: 0 auto;
background-color: gold;
position: absolute;
}
</style>2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
计算方式 800 = 200 + 0 + 0 + auto + auto;,auto的意思就是交给浏览器处理。
sticky 粘性定位
sticky 是一个大家期待已久的属性,可以看做是相对定位和固定(绝对)定位的结合体,它允许被定位的元素表现得像相对定位一样,直到它滚动到某个阈值点,当达到这个阈值点时, 就会变成固定(绝对)定位。
z-index 层叠关系
z-index 属性用来设置定位元素的层叠顺序仅对定位元素有效,默认值是0,可以设置正整数、负整数。
- 如果是兄弟关系:
z-index越大,层叠在越上面,z-index相等,写在后面的那个元素层叠在上面 - 如果不是兄弟关系: 各自从元素自己以及祖先元素中,找出最邻近的2个定位元素进行比较,而且这2个定位元素必须有设置
z-index的具体数值
<style>
.item{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
position: fixed;
}
.box1{
background-color: aqua;
}
.box2{
left: 20px;
top: 20px;
background-color: red;
z-index: 1; /* 层叠关系 */
}
.box3{
left: 40px;
top: 40px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class="item box1">1</div>
<div class="continer">
<div class="item box2">2</div>
</div>
<div class="item box3">3</div>
</body>2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
弹性盒子布局 Flexbox
Flexbox翻译为弹性盒子:是一种用于按行或按列布局元素的一维布局方法。元素可以膨胀以填充额外的空间, 收缩以适应更小的空间。通常我们使用Flexbox来进行布局的方案称之为flex布局(flex layout)。
flex布局的重要概念:
- 开启了 flex 布局的元素叫
flex container,flex container里面的直接子元素叫做flex item。 - 设置
display属性为flex或者inline-flex可以成为flex containercssdisplay: flex ; /* 生成一个块级的Flex容器 */ display: inline-flex; /* 生成一个行级的Flex容器 */1
2
flex container的相关属性,控制盒子的 摆放流向、摆放顺序、盒子的宽度和高度、水平和垂直方向的对齐、是否允许折行
flex-direction:row; /* 控制摆放方向 */
flex-wrap:wrap; /* 是否允许换行 */
flex-flow: row wrap; /* flex-flow 属性是 flex-direction 和 flex-wrap 的简写。 */
justify-content: flex-start; /* 决定了 flex items 在 主轴 上的对齐方式 */
align-items: center; /* 决定了 flex items 在 侧轴 上的对齐方式 */
align-content: center; /* 决定了多行 flex items 在 cross axis 上的对齐方式,用法与 justify-content 类似 */2
3
4
5
6

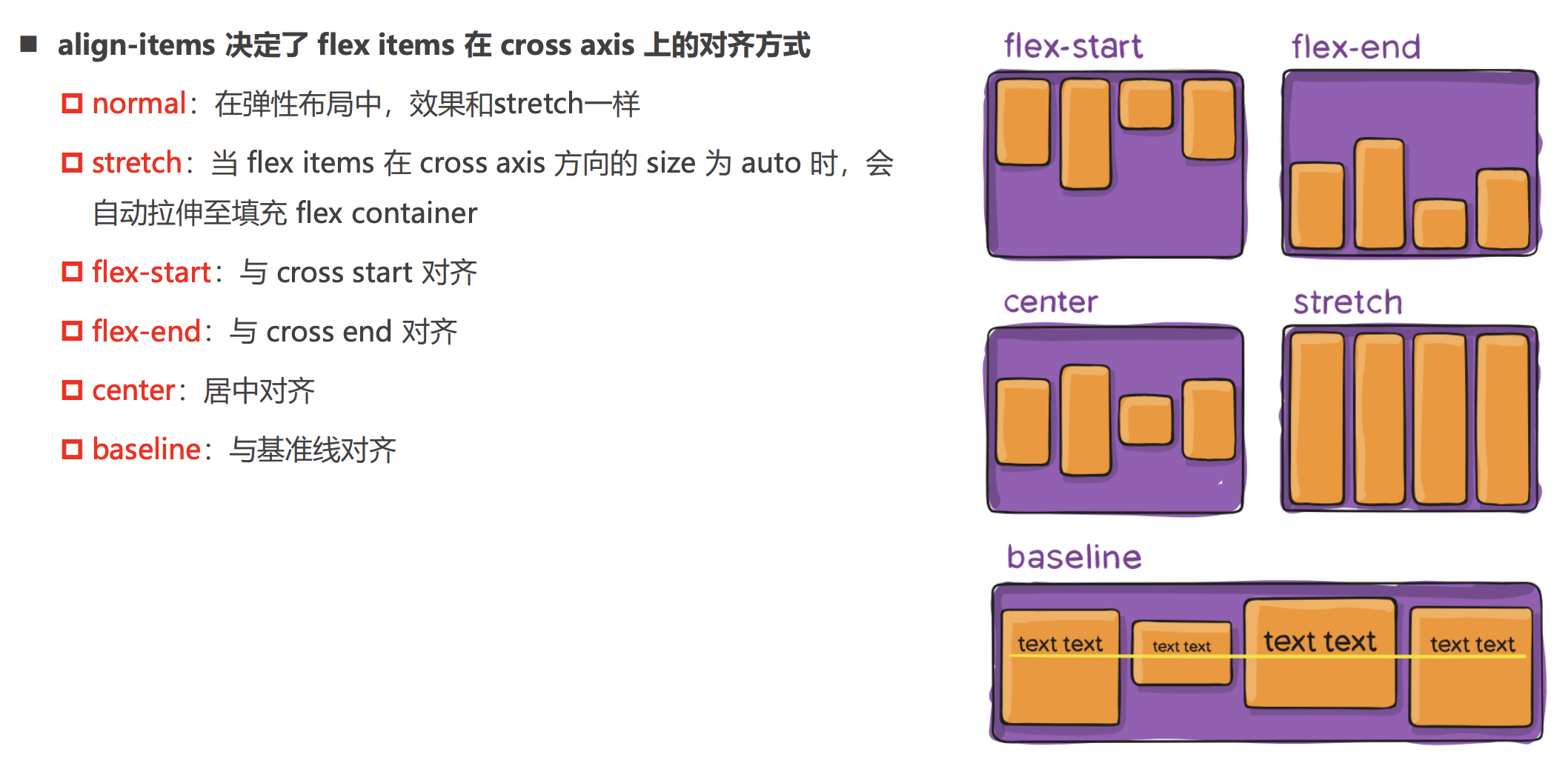

flex item的相关属性
flex-grow: 0; /* 决定 flex items 如何扩展(拉伸/成长),默认值是 0 */
flex-shrink: 0; /* 决定 flex items 如何收缩(缩小),默认是 1 */
flex-basis: 100px; /* 设置 flex items 在 main axis 方向上的 基础大小,默认auto */
align-self: flex-end; /* 针对单个元素的对齐方式, 默认值auto */
order: 1; /* 单个元素使用,决定了 flex items 的排布顺序 */
flex: 0 0 100px; /* flex-grow || flex-shrink || flex-basis 的简写 */2
3
4
5
6
- flex布局中最后一行item的处理,添加 i 的个数需要是 行数-2
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<style>
.container{
width: 500px;
background-color: orange;
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
justify-content: space-between;
}
.item{
width: 110px;
height: 140px;
}
.container > i{ /* 因为i没有设置高度,所以不会显示 */
width: 110px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="item item1"></div>
<div class="item item2"></div>
<div class="item item3"></div>
<div class="item item4"></div>
<div class="item item5"></div>
<div class="item item6"></div>
<div class="item item7"></div>
<!-- 添加 i 的个数需要是行数-2,这里一行4个item,需要添加2个i标签 -->
<i></i>
<i></i>
</div>
<script>
function getRandomColor() {
return `rgb(${Math.random()*255}, ${Math.random()*255}, ${Math.random()*255})`
}
const itemEls = document.querySelectorAll(".item")
for (const item of itemEls) {
item.style.backgroundColor = getRandomColor()
}
</script>
</body>
</html>2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
Grid布局
/* 生成一个块级的Grid容器 */
display: grid ;
/*
grid-template-columns 有几个值,代表有几列
grid-template-rows: 有几个值,代表有几行
有三种表示形式
*/
grid-template-columns: 100px 200px 300px 400px;
grid-template-rows: 100px 50px;
grid-template-columns: 30% 20% auto;
grid-template-rows: 100px auto;
grid-template-columns: 100px 1fr 1fr;
grid-template-rows: 100px 1fr;
/* 修改单个网格布局大小 ,以分割线做区分,分割线以 1 开始*/
.a{
grid-column-start: 1;
grid-row-start: 1;
grid-row-end: 3;
grid-column-end: 3;
}
/* 等价于 */
.a{
grid-area:1/1/3/3;
}
/* 设置行和列之间的间距 ,gap 同时设置行和列的间距*/
row-gap: 10px;
column-gap: 10px;
gap: 10px 10px;
/* 行方向是否填满整个块级元素, 默认填满 */
align-items: stretch;
/* 列方向是否填满整个块级元素,默认填满 */
justify-items: stretch;
/* 单独设置某个item 在列方向的位置 */
align-self: center;
/* 单独设置某个item 在行方向的位置 */
justify-self: center;
/* 当元素不会占满整个容器的时候,使用align-content 和 justify-content */2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
浮动
1. 浮动都会让元素脱离标准流,可以通过`float`属性让元素产生浮动效果,取值有`none、left、right`
2. 浮动元素碰到父元素边界、浮动元素、未浮动的元素才停下来
3. 相邻浮动的块元素可以并在一行,超出父级宽度换行
4. 浮动让行内元素或块元素自动转化为行内块元素
5. 浮动元素后面没有浮动的元素会占据它的位置,没有浮动的元素内的文字会避开浮动的元素,形成文字饶图的效果
6. 父元素没有高度时,浮动的元素无法撑开父元素,需要清除浮动
7. 浮动元素之间没有垂直margin的合并2
3
4
5
6
7
- 浮动高度塌陷问题 由于浮动元素脱离了标准流,变成了脱标元素,所以不再向父元素汇报高度。**父元素计算总高度时,就不会计算浮动子元素的高度,导致了高度坍塌的问题。**解决父元素高度坍塌问题的过程,一般叫做清浮动(清理浮动、清除浮动),清浮动的目的是 让父元素计算总高度的时候,把浮动子元素的高度算进去
清除浮动的几种方式
/* 1、父级上增加属性 overflow:hidden */
.box{
overflow:"hidden";
}
/* 2、最后一个子元素的后面加一个空的div,样式属性clear:both <不推荐使用> */
<div style="clear:both"></div>
/* 3、使用成熟的清浮动样式类 clearfix */
.clearfix:after,.clearfix:before{ content: "";display: table;}
.clearfix:after{ clear:both;}
.clearfix{zoom:1;}
/* 第二种 clearfix 清除方式 */
.con2{... overflow:hidden}
或者
<div class="con2 clearfix">2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16